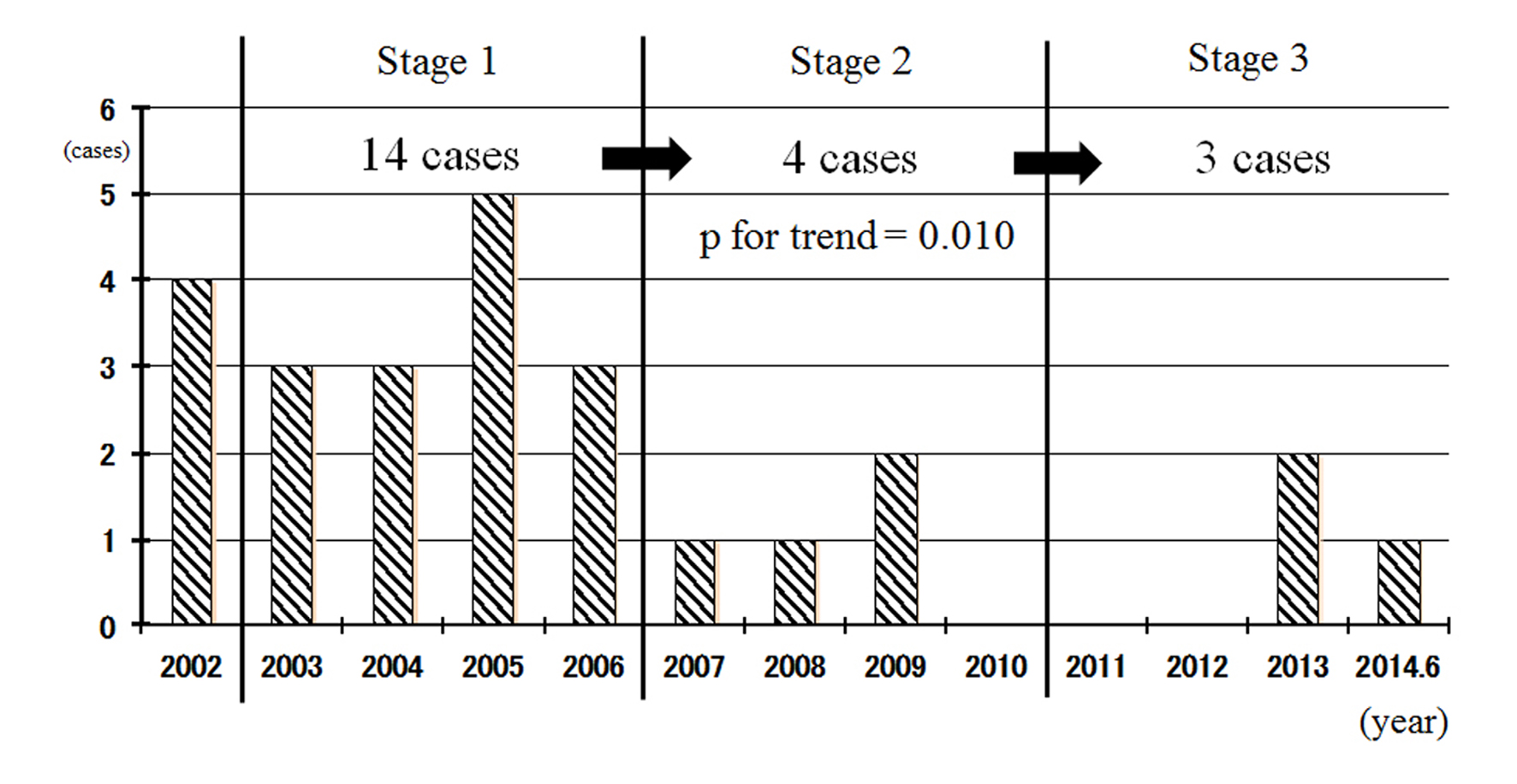
Figure 1. Association between non-smoking areas in a hospital and the in-hospital onset of AMI. Non-smoking areas throughout the building (stage 1, 2003 - 2006), smoking was banned throughout the entire hospital at the early (stage 2, 2007 - 2010) and late (stage 3, 2011 - 2014) phases.