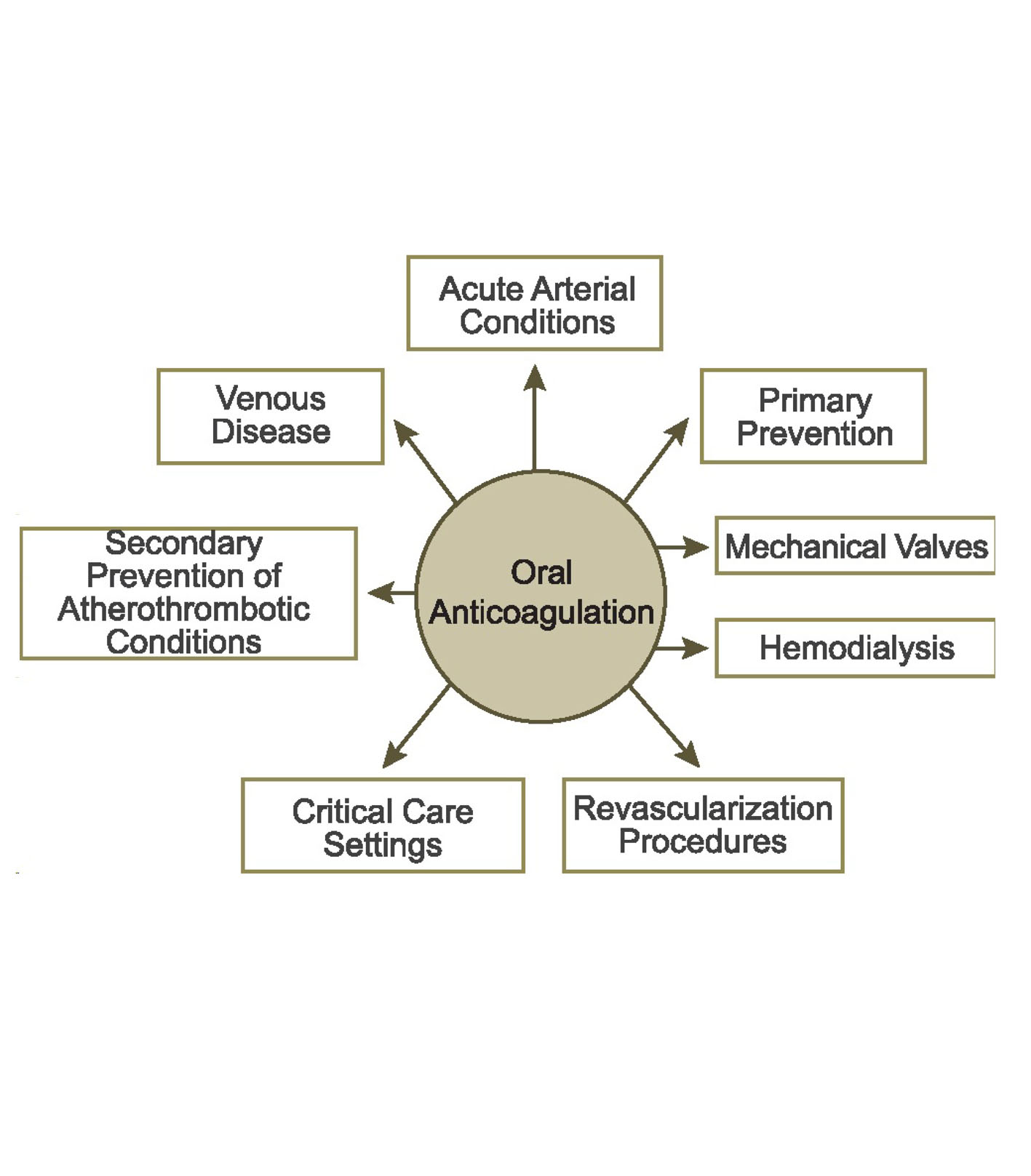
Figure 1. Clinical settings for oral anticoagulation. Clinical questions about the management of the NOACs exist in each of these settings.
| Cardiology Research, ISSN 1923-2829 print, 1923-2837 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Cardiol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.cardiologyres.org |
Review
Volume 6, Number 3, June 2015, pages 267-277
Unmet Needs in Anticoagulant Therapy: Potential Role of Rivaroxaban
Figures

Tables
| Trial | Clinical question(s) to be addressed | Arms | Targeted enrollment |
|---|---|---|---|
| *P2Y12 inhibitor such as clopidogrel (75 mg QD). ACS: acute coronary syndrome; AF: atrial fibrillation; ASA: acetylsalicylic acid; DAPT: dual antiplatelet therapy; LA: left atrial; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; SVT: superficial vein thrombosis; UFH: unfractionated heparin; VKA: vitamin K antagonist; VTE: venous thromboembolic events. | |||
| Stroke prevention in patients with AF | |||
| VENTURE-AF NCT01729871 | Does rivaroxaban need to be stopped prior to catheter ablation in patients with non-valvular AF? | Rivaroxaban 20 mg QD VKA (INR 2.0-3.0) | 250 |
| X-TRA NCT01674647 | Does treatment with rivaroxaban regress LA thrombi in patients with non-valvular AF or atrial flutter? | Rivaroxaban 20 mg QD | 60 |
| VTE treatment | |||
| EINSTEIN CHOICE NCT02064439 | Can a lower dose (10 mg) of rivaroxaban be used for the long-term prevention of VTE, and is this or 20 mg rivaroxaban superior to ASA? | Rivaroxaban 10 mg QD Rivaroxaban 20 mg QD ASA 100 mg QD | 2,850 |
| EINSTEIN Junior NCT01684423 | Can rivaroxaban be safely used in children? | Rivaroxaban (age and weight adjusted) Standard of care | 50 |
| Superficial vein thrombosis NCT01499953 | Can rivaroxaban be used to treat SVT? | Rivaroxaban 20 mg QD | 506 |
| Prevention of VTE | |||
| MARINER NCT02111564 | Can rivaroxaban reduce the risk of post-hospital discharge symptomatic VTE in patients hospitalized for acute medical illness? | Rivaroxaban 10 mg QD or 7.5 mg QD (adjusted for creatine clearance) Placebo | 8,000 |
| EPCAT II NCT01720108 | Is rivaroxaban more effective than ASA for extended prophylaxis of VTE? | Rivaroxaban 10 mg QD Fondaparinux 2.5 mg QD | 3,436 |
| Therapeutic approaches for patients with coronary disease | |||
| GEMINI ACS 1 NCT02293395 | Can rivaroxaban, in combination with a single antiplatelet agent, be used for secondary prevention in patients with ACS? | Study design not released at the time of publication | 3,000 |
| X-PLORER NCT01442792 | Can rivaroxaban prevent thrombosis and related adverse ischemic events during elective PCI? | Rivaroxaban 20 mg QD Rivaroxaban 10 mg QD Rivaroxaban 10 mg QD + UFH 50 IU/kg bolus UFH 70-100 IU/kg bolus | 106 |
| PIONEER AF-PCI NCT01830543 | Should rivaroxaban be used over warfarin in patients who have undergone PCI and are on antiplatelet therapy? If so, what is the optimal rivaroxaban dose and antiplatelet regimen for these patients? | Rivaroxaban 15 mg QD + P2Y12 inhibitor* Rivaroxaban 2.5 mg BID + DAPT VKA + DAPT | 2,100 |
| Trial | Clinical question(s) to be addressed | Arms | Estimated enrollment |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASA: acetylsalicylic acid; CAD: coronary artery disease; ESUS: embolic stroke of undetermined source; HIT: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; PAD: peripheral artery disease; TIA: transient ischemic attack. | |||
| Secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease | |||
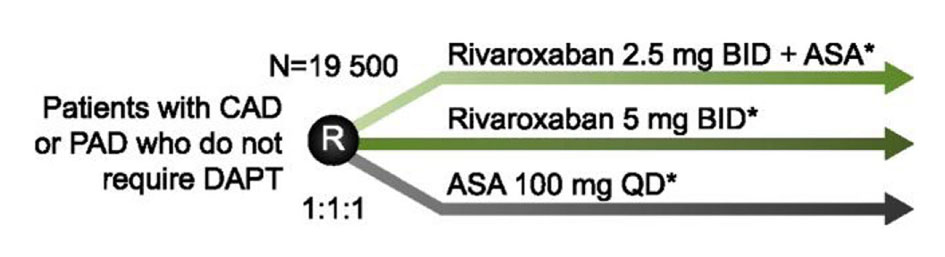
| COMPASS NCT01776424 | Does rivaroxaban provide additional cardioprotective benefits to high-risk patients? Should rivaroxaban be used alone or in combination with ASA in patients with CAD or PAD? | Rivaroxaban 2.5 mg BID + ASA Rivaroxaban 5.0 mg BID ASA 100 mg QD | 19,500 |
| Heart failure | |||
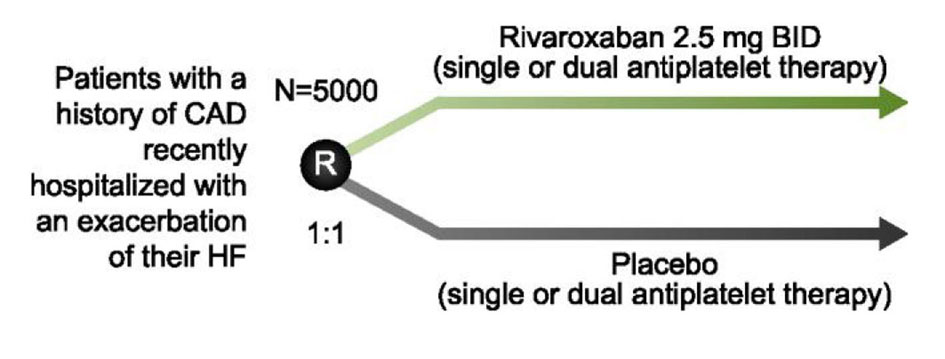
| COMMANDER-HF NCT01877915 | Does adding low-dose rivaroxaban to optimal medical therapy improve outcomes in heart failure? | Rivaroxaban 2.5 mg BID + single or dual antiplatelet therapy Single or dual antiplatelet therapy | 5,000 |
| Confirmed or suspected HIT | |||
| Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia NCT01598168 | Can rivaroxaban be used to treat HIT? | Rivaroxaban 15 mg BID until HIT excluded, followed by rivaroxaban 20 mg QD | 200 |
| Stroke prevention in patients with ESUS | |||
| NAVIGATE ESUS NCT02313909 | Is rivaroxaban more effective than ASA atreducing the risk of recurrent stroke and systemic embolism in patients with a recent ESUS? | Rivaroxaban 15 mg QD ASA 100 mg QD | 7,000 |
| Treatment of high-risk patients with non-disabling cerebrovascular events | |||
| TRACE NCT01923818 | Should rivaroxaban be used over ASA in patients following TIA or minor ischemic stroke? | ASA 100 mg QD Rivaroxaban 5 mg Rivaroxaban 10 mg | 3,700 |