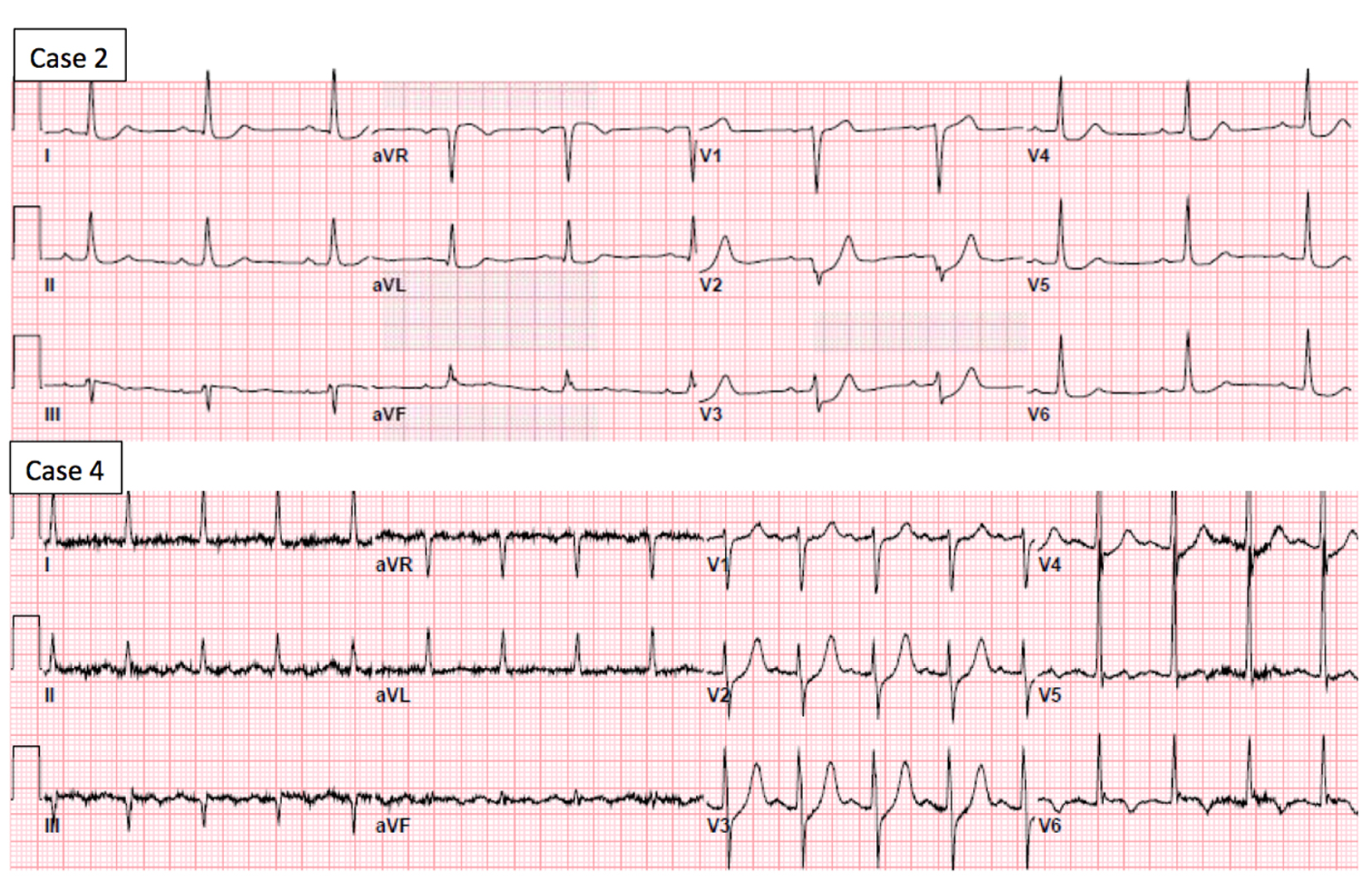
Figure 1. Electrocardiogram of case 2 shows up-sloping ST-segment depression in leads V2 and V3, and horizontal ST-depression in leads V4 to V6, I and aVL. Electrocardiogram of case 4 shows up-sloping ST-segment depression in leads V2 and V4.
| Cardiology Research, ISSN 1923-2829 print, 1923-2837 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Cardiol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.cardiologyres.org |
Original Article
Volume 6, Number 4-5, October 2015, pages 306-310
Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Up-Sloping ST-Segment Depression in Patients With Non-ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Figure

Tables
| Up-sloping ST depression (n = 6) | Non-up-sloping ST depression (n = 103) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| aInterval from presentation to catheterization. Data are expressed as number (percentage) or median (interquartile range). CAD: coronary artery disease; MI: myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; TIMI: thrombolysis in myocardial infarction; CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting. | |||
| Baseline characteristics and risk factors | |||
| Age (years) | 59 (49 - 69) | 67 (60 - 78) | 0.24 |
| Men (%) | 5 (83) | 63 (61) | 0.41 |
| Hypertension (%) | 4 (67) | 80 (78) | 0.62 |
| Diabetes (%) | 1 (17) | 38 (37) | 0.42 |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | 2 (33) | 62 (60) | 0.23 |
| Previous MI (%) | 1 (17) | 16 (16) | 1 |
| Previous PCI (%) | 2 (33) | 30 (29) | 1 |
| TIMI risk score 5 - 7 | 2 (33) | 46 (45) | 0.69 |
| Hemodynamic, laboratory data and echocardiogram findings | |||
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 120 (114 - 132) | 144 (125 - 161) | 0.04 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 90 (78 - 106) | 81 (69 - 95) | 0.51 |
| Killip class > 1 on admission (%) | 1 (17) | 12 (12) | 0.54 |
| Peak troponin I (µg/L) | 73.2 (15.6 - 253) | 3.04 (0.27 - 11.0) | 0.006 |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction (%) | 43 (39 - 49) | 60 (45 - 62) | 0.04 |
| Angiographic findings and in-hospital events | |||
| Intervala (days) | 0.4 (0.3 - 0.8) | 1.0 (0.3 - 2.1) | 0.22 |
| Obstructive CAD (%) | 6 (100) | 93 (90) | 1 |
| Multi-vessel disease (%) | 4 (67) | 71 (69) | 1 |
| Left main/three-vessel disease (%) | 2 (33) | 43 (42) | 1 |
| Pre-procedural TIMI grade 0 - 1 flow (%) | 3 (50) | 32 (31) | 0.38 |
| Angiographic thrombus (%) | 6 (100) | 48 (47) | 0.01 |
| High-grade thrombus (TIMI grade 4 - 5) (%) | 4 (67) | 24 (23) | 0.04 |
| In-hospital revascularization (%) | 6 (100) | 77 (75) | 0.33 |
| In-hospital PCI (%) | 5 (83) | 60 (58) | 0.4 |
| In-hospital CABG (%) | 1 (17) | 17 (17) | 1 |
| In-hospital outcomes | |||
| In-hospital all-cause death (%) | 2 (33) | 0 (0) | 0.003 |
| In-hospital heart failure (%) | 1 (17) | 15 (15) | 1 |
| In-hospital cardiogenic shock (%) | 1 (17) | 3 (3) | 0.22 |
| Length of stay (days) | 7.6 (5.2 - 13.5) | 5.8 (3.0 - 9.4) | 0.22 |
| Case | Age | Sex | Symptom duration | Leads with ST depression | Intervala | IRA | TIMI flow | Collateral grade | No. of vessels | Procedure | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aInterval from presentation to catheterization. bIntermittent crescendo chest pain. cSevere stenosis (> 95%) in all three major coronary arteries. IRA: infarct-related artery; TIMI: thrombolysis in myocardial infarction; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; CABG: coronary artery bypass grafting; LAD: left anterior descending; LCX: left circumflex. | |||||||||||
| 1 | 66 | M | 45 min | V3-V6 | 9 h | LAD | 2 | 0 | 1 VD | PCI | - |
| 2 | 70 | M | 90 min | V2-V6, I, aVL | 7 h | LAD | 0 | 2 | 2 VD | PCI | - |
| 3 | 47 | M | 1 day | V4-V6, I, II, aVF | 34 h | LAD | 3 | 0 | 1 VD | PCI | - |
| 4 | 91 | M | 12 h | V2-V4 | 9 h | LCX | 0 | 0 | 3 VD | PCI | Death |
| 5 | 48 | F | 2 daysb | V2-V6, I, aVL | 4 h | LCX | 0 | 1 | 2 VD | PCI | Death |
| 6 | 52 | M | 2 daysb | V4-V5 | 23 h | 3 VDc | 2 | 0 | 3 VD | CABG | - |